Email is a service that allows us to send the message in electronic mode over the internet. It offers an efficient, inexpensive, and real-time means of distributing information among people.
E-Mail Address
Each user of the email is assigned a unique name for his email account. This name is known as the E-mail address. Different users can send and receive messages according to the e-mail address.
E-mail is generally of the form username@domainname. For example, webmaster@tutorialspoint.com is an e-mail address where webmaster is the username and tutorialspoint.com is the domain name.
-
The username and the domain name are separated by @ (at) symbol.
-
E-mail addresses are not case sensitive.
-
Spaces are not allowed in e-mail address.
- The username and the domain name are separated by @ (at) symbol.
- E-mail addresses are not case sensitive.
- Spaces are not allowed in e-mail address.
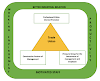
E-mail Message Components
E-mail message comprises of different components: E-mail Header, Greeting, Text, and Signature. These components are described in the following diagram:

E-mail Header
The first five lines of an E-mail message is called E-mail header. The header part comprises of following fields:
-
From
-
Date
-
To
-
Subject
-
CC
-
BCC
From
Date
To
Subject
CC
BCC
From
The From field indicates the sender’s address i.e. who sent the e-mail.
Date
The Date field indicates the date when the e-mail was sent.
To
The To field indicates the recipient’s address i.e. to whom the e-mail is sent.
Subject
The Subject field indicates the purpose of e-mail. It should be precise and to the point.
CC
CC stands for Carbon copy. It includes those recipient addresses whom we want to keep informed but not exactly the intended recipient.
BCC
BCC stands for Black Carbon Copy. It is used when we do not want one or more of the recipients to know that someone else was copied on the message.
Greeting
The greeting is the opening of the actual message. Eg. Hi, Sir or Hi Guys etc.
Text
It represents the actual content of the message.
Signature
This is the final part of an e-mail message. It includes the Name of the Sender, Address, and Contact Number.
Advantages
An E-mail has proved to be a powerful and reliable medium of communication. Here are the benefits of E-mail:
-
Reliable
-
Convenience
-
Speed
-
Inexpensive
-
Printable
-
Global
-
Generality
Reliable
Convenience
Speed
Inexpensive
Printable
Global
Generality
Reliable
Many of the mail systems notify the sender if the e-mail message was undeliverable.
Convenience
There is no requirement for stationery and stamps. One does not have to go to the post office. But all these things are not required for sending or receiving a mail.
Speed
E-mail is very fast. However, the speed also depends upon the underlying network.
Inexpensive
The cost of sending an e-mail is very low.
Printable
It is easy to obtain a hardcopy of an e-mail. Also, an electronic copy of an e-mail can also be saved for records.
Global
E-mail can be sent and received by a person sitting across the globe.
Generality
It is also possible to send graphics, programs, and sounds with an e-mail.
Disadvantages
Apart from several benefits of E-mail, there also exist some disadvantages as discussed below:
-
Forgery
-
Overload
-
Misdirection
-
Junk
-
No response
Forgery
Overload
Misdirection
Junk
No response
Forgery
E-mail doesn’t prevent forgery, that is, someone impersonating the sender, since the sender is usually not authenticated in any way.
Overload
The convenience of E-mail may result in a flood of mail.
Misdirection
It is possible that you may send e-mail to an unintended recipient.
Junk
Junk emails are undesirable and inappropriate emails. Junk emails are sometimes referred to as spam.
No Response
It may be frustrating when the recipient does not read the e-mail and respond on a regular basis.
E-mail System
The E-mail system comprises of the following three components:
-
Mailer
-
Mail Server
-
Mailbox
Mailer
Mail Server
Mailbox
Mailer
It is also called a mail program, mail application, or mail client. It allows us to manage, read, and compose e-mail.
Mail Server
The function of the mail server is to receive, store, and deliver the email. It is a must for mail servers to be running all the time because if it crashes or is down, email can be lost.
Mailboxes
Mailbox is generally a folder that contains emails and information about them.
Working of E-mail
Email working follows the client-server approach. In this client is the mailer i.e. the mail application or mail program and the server is a device that manages emails.
The following example will take you through the basic steps involved in sending and receiving emails and will give you a better understanding of the working of email system:
-
Suppose person A wants to send an email message to person B.
-
Person A composes the messages using a mailer program i.e. mail client and then select the Send option.
-
The message is routed to Simple Mail Transfer Protocol to person B’s mail server.
-
The mail server stores the email message on disk in an area designated for person B.
The disk space area on mail server is called mail spool.
-
Now, suppose person B is running a POP client and knows how to communicate with B’s mail server.
-
It will periodically poll the POP server to check if any new email has arrived for B.As in this case, person B has sent an email for person B, so email is forwarded over the network to B’s PC. This is message is now stored on person B’s PC.
The following diagram gives a pictorial representation of the steps discussed above:

Suppose person A wants to send an email message to person B.
Person A composes the messages using a mailer program i.e. mail client and then select the Send option.
The message is routed to Simple Mail Transfer Protocol to person B’s mail server.
The mail server stores the email message on disk in an area designated for person B.
Now, suppose person B is running a POP client and knows how to communicate with B’s mail server.
It will periodically poll the POP server to check if any new email has arrived for B.As in this case, person B has sent an email for person B, so email is forwarded over the network to B’s PC. This is message is now stored on person B’s PC.

Creating Email Account
There are various email service providers available such as Gmail, Hotmail, Gmail, Rediff mail, etc. Here we will learn how to create an account using Gmail.
-
Open gmail.com and click create an account.
-
Now a form will appear. Fill your details here and click Next Step.

-
This step allows you to add your picture. If you don’t want to upload now, you can do it later. Click Next Step.
-
Now a welcome window appears. Click Continue to Gmail.
-
Wow!! You are done with creating your email account with Gmail. It’s that easy. Isn’t it?
-
Now you will see your Gmail account as shown in the following image:
 Key Points:
Key Points:
-
Gmail manages the mail into three categories namely Primary, Social, and Promotions.
-
Compose option is given at the right to compose an email message.
-
Inbox, Starred, Sent Mail, Drafts options are available on the left pane which allows you to keep track of your emails.
Open gmail.com and click create an account.
Now a form will appear. Fill your details here and click Next Step.

This step allows you to add your picture. If you don’t want to upload now, you can do it later. Click Next Step.
Now a welcome window appears. Click Continue to Gmail.
Wow!! You are done with creating your email account with Gmail. It’s that easy. Isn’t it?
Now you will see your Gmail account as shown in the following image:

Gmail manages the mail into three categories namely Primary, Social, and Promotions.
Compose option is given at the right to compose an email message.
Inbox, Starred, Sent Mail, Drafts options are available on the left pane which allows you to keep track of your emails.
Composing and Sending Email
Before sending an email, we need to compose a message. When we are composing an email message, we specify the following things:
-
Sender’s address in To field
-
Cc (if required)
-
Bcc (if required)
-
The subject of email message
-
Text
-
Signature
You should specify the correct email address; otherwise it will send an error back to the sender.
Once you have specified all the above parameters, It’s time to send the email. The mailer program provides a Send button to send an email, when you click Send, it is sent to the mail server and a message mail sent successfully is shown at the above.
Sender’s address in To field
Cc (if required)
Bcc (if required)
The subject of email message
Text
Signature
Reading Email
Every email program offers you an interface to access email messages. Like in Gmail, emails are stored under different tabs such as primary, social, and promotion. When you click one tab, it displays a list of emails under that tab.
In order to read an email, you just have to click on that email. Once you click a particular email, it gets opened.
The opened email may have some file attached to it. The attachments are shown at the bottom of the opened email with an option called download attachment.
Replying Email
After reading an email, you may have to reply to that email. To reply to an email, click the Reply option shown at the bottom of the opened email.
Once you click on Reply, it will automatically copy the sender’s address into the To field. Below the To field, there is a text box where you can type the message.
Once you are done with entering the message, click the Send button. It’s that easy. Your email is sent.
Forwarding Email
It is also possible to send a copy of the message that you have received along with your own comments if you want. This can be done using the forward button available in mail client software.
The difference between replying and forwarding an email is that when you reply a message to a person who has to send the mail but while forwarding you can send it to anyone.
When you receive a forwarded message, the message is marked with a > character in front of each line and the Subject: field is prefixed with FW.
Deleting Email
If you don’t want to keep email into your inbox, you can delete it by simply selecting the message from the message list and clicking delete or pressing the appropriate command.
Some mail clients offer the deleted emails to be stored in a folder called deleted items or trash from where you can recover a deleted email.
E-mail Features
Now a day, the mail client comes with enhanced features such as attachment, address book, and MIME support. Here in this chapter, we will discuss all of these features which will give you a better understanding of added feature of a mail client program.
Attachment
The ability to attach a file(s) along with the message is one of the most useful features of email. The attachment may be a word document, PowerPoint presentation, audio/video files, or images.
- In order to attach a file(s) to an email, click the attach button. As a result, a dialog box appears asking for specifying the name and location of the file you want to attach.
- Once you have selected the appropriate file, it is attached to the mail.
- Usually, a paper clip icon appears in the email which indicates that it has an attachment.
- When adding an attachment it is better to compress the attached files so as to reduce the file size and save transmission time as sending and downloading large files consumes a lot of space and time.
Address Book
The address book feature of a mail program allows the users to store information about the people whom they communicate regularly by sending emails. Here are some of the key features of an Address book:
- The address book includes the nicknames, email addresses, phone numbers, etc. of the people.
- Using an address book allows us not to memorize the email of the address of a person, you just have to select the recipient name from the list.
- When you select a particular name from the list, the corresponding email address link automatically gets inserted into the To: field.
- The address book also allows creating a group so that you can send an email to every member of the group at once instead of giving each person an email address one by one.
MIME Types
MIME is an acronym of Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions. MIME-compliant mailer allows us to send files other than simple text i.e. It allows us to send audio, video, images, document, and pdf files as an attachment to an email.
Suppose if you want to send a word processor document that has a group of tabular columns with complex formatting. If we transfer the file as text, all the formatting may be lost. MIME-compliant mailer takes care of messy details and the message arrives as desired.
The following table describes commonly used MIME Types:
| 1. | Type | Subtype | Description | File extension(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2. | Application | postscript tex troff | Printable postscript document TEX document Printable troff document | .eps, .ps .tex .t, .tr, .roff |
| 3. | Audio | aiff au midi real audio | Apple sound Sun Microsystems sound Musical Instrument Digital Interface Progressive Network sound | .aif, .aiff,.aifc .au, .snd .midi, .mid .ra, .ram |
| 4. | image | gif jpeg png tariff | Graphics Interchange Format Joint Photographic Experts Group Portable Network Graphics Tagged Image Modeling Language | .gif .jpeg, .jpg, .jpe .png .tiff, .tif |
| 5. | Model | VRML | Virtual Reality Modelling Language | .wrl |
| 6. | Text plain sgml | HTML | Hyper Text Markup Language Unformatted text Standard Generalized Markup language | .html, .htm .txt .sgml |
| 7. | Video | avi MPEG QuickTime sgi-movie | Microsoft Audio Video Interleaved Moving Pictures Expert Group Apple QuickTime movie silicon graphic movie | .avi .mpeg, .mpg .qt, .mov .movie |
E-mail Security
E-mail Hacking
Email hacking can be done in any of the following ways:
- Spam
- Virus
- Phishing
Spam
E-mail spamming is an act of sending Unsolicited Bulk E-mails (UBI) which one has not asked for. Email spams are the junk mails sent by commercial companies as an advertisement of their products and services.
Virus
Some emails may incorporate files containing a malicious script which when run on your computer may lead to destroying your important data.
Phishing
Email phishing is an activity of sending emails to a user claiming to be a legitimate enterprise. Its main purpose is to steal sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details.
Such emails contain a link to websites that are infected with malware and direct the user to enter details at a fake website whose look and feels are the same to legitimate ones.
E-mail Spamming and Junk Mails
Email spamming is an act of sending Unsolicited Bulk E-mails (UBI) which one has not asked for. Email spams are the junk mails sent by commercial companies as an advertisement of their products and services.
Spams may cause the following problems:
- It floods your e-mail account with unwanted e-mails, which may result in loss of important e-mails if the inbox is full.
- Time and energy are wasted in reviewing and deleting junk emails or spams.
- It consumes the bandwidth that slows the speed with which emails are delivered.
- Some unsolicited emails may contain a virus that can cause harm to your computer.
Blocking Spams
The following ways will help you to reduce spams:
- While posting letters to newsgroups or mailing lists, use a separate e-mail address than the one you used for your personal e-mails.
- Don’t give your email address on the websites as it can easily be spammed.
- Avoid replying to emails which you have received from unknown persons.
- Never buy anything in response to spam that advertises a product.
E-mail Cleanup and Archiving
In order to have a light-weighted Inbox, it’s good to archive your inbox from time to time. Here I will discuss the steps to clean up and archive your Outlook inbox.
- Select the File tab on the main pane.
- Select the Cleanup Tools button on the account information screen.
- Select Archive from the cleanup tools drop-down menu.
- Select Archive this folder and all subfolders option and then click on the folder that you want to archive. Select the date from the Archive items older than the list. Click Browse to create a new .pst file name and location. Click OK.






0 Comments